What aspects of Aboriginal cultural tourism experiences are wellness transformation visitors looking for?
What makes tourism experiences desirable to any traveller is often intangible and varies across visitors. Market research has identified numerous aspects of tourism products that contribute to visitor satisfaction.
Some wellness transformation travellers indicate that they want to expand their horizons and find new meaning in their lives by interacting with different cultures and being exposed to new knowledge, beliefs and worldviews. They value learning from people unlike themselves and aim to understand how the latter see and interpret the world. Many seek cultural tourism experiences as part of an intangible spiritual journey (one of the key elements of wellness) as they mindfully pursue a quest to better understand themselves and the nature of human existence.6 These two dimensions are well worth highlighting when developing new experiences, as they appeal to the more sophisticated cultural visitors often associated with the wellness-transformation market in particular.
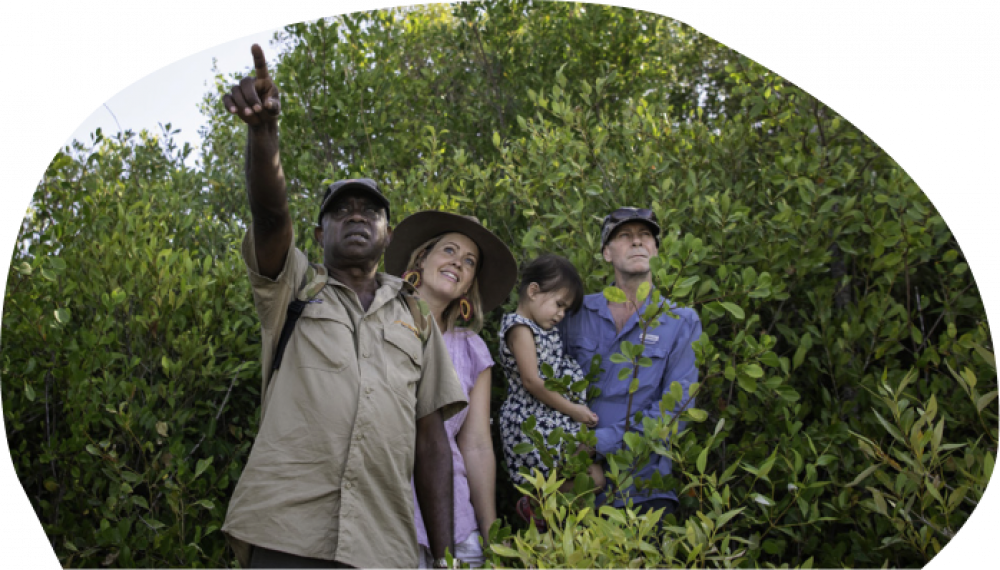


Although they are interrelated, two key concepts that mainly contribute to the appeal of Aboriginal tourism experiences based in the NT are sought after by wellness transformation travellers. These two concepts are discussed in both international academic and industry research investigating successful Aboriginal tourism product design.
They are:
- The unique and genuine nature of the experience.7
- The nature and spread of connections between the components of the experience that reinforce each other.
Why do wellness transformation visitors seek unique Aboriginal cultural experiences and how can their genuine nature quality be
communicated to those travellers?
What makes a visitor experience unique or genuine is a tricky topic because it can mean different things to different people.
All people involved in providing those experiences (Aboriginal hosts, guides, businesses, experts, destinations, etc.) and the
visitors themselves have their own perspectives regarding what is ‘real’ or genuine. Yet, this dimension is recognised as very
important to wellness transformation visitors and impacts the reputation of cultural tourism products.
The wellness tourism sector has increasingly stated that many international wellness visitors were dissatisfied with many socalled ‘First Nations experiences’ around the world. They claim that several wellness international visitors find such experiences contrived, unnatural or obviously staged (not genuine nor spontaneous or sincere).
They concluded that wellness transformation visitors increasingly seek genuine Aboriginal experiences where they can share genuine living culture linked to place, country and spirituality.


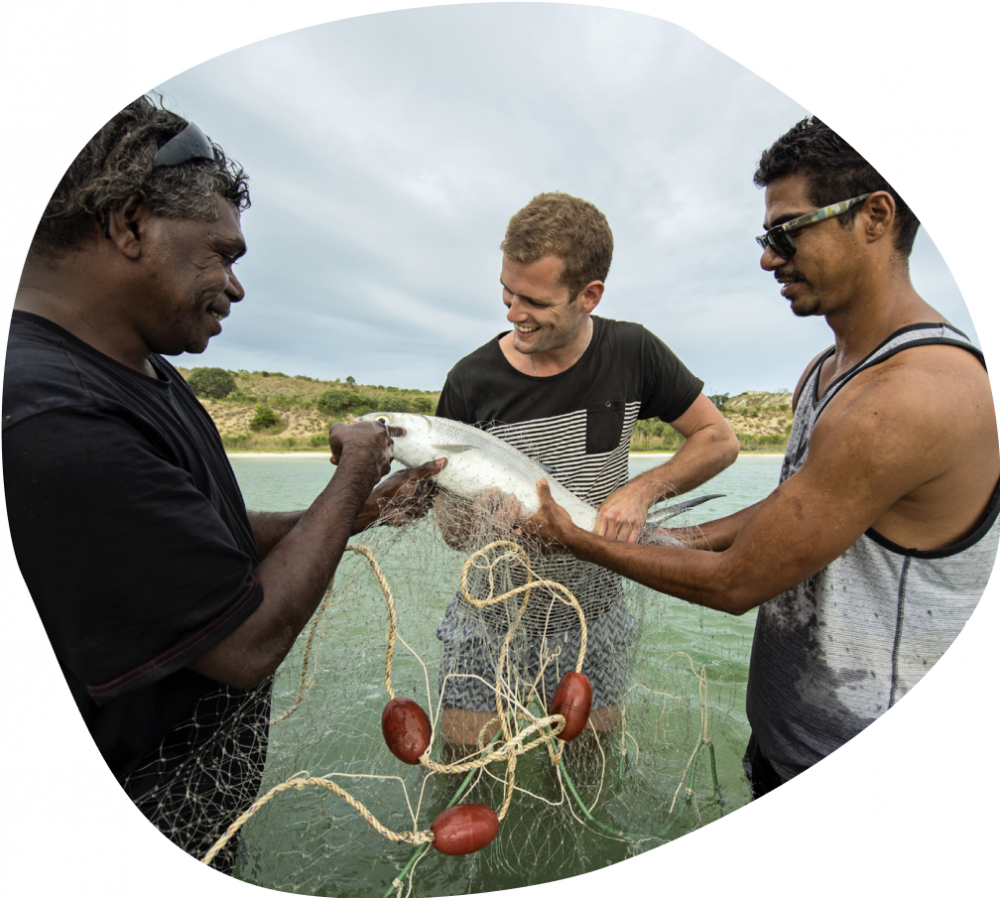
Experiences on offer in destinations such as the NT are increasingly recognised and sought by wellness transformation travellers because visitors recognise the genuine nature of the connections between culture, place, landscape and tradition. Aboriginal tourism businesses must strive to show and communicate to wellness transformation visitor markets what makes their product unique and genuine.
What types of ‘connections’ between the components of the cultural experience contribute to the satisfaction of wellness transformation visitors?
Wellness visitors seek holistic experiences (which means they combine physical, mental, and spiritual wellbeing aspects) that are unusual to them and will challenge their everyday worldviews as well as confront their senses and their values.
Their quest for transformation is more likely to occur if they are exposed simultaneously to multiple and connected experiences as well as overlapping sensations. Typically, this means experiencing at once new cultures, new landscapes, new food or cuisines capable of affecting many of their senses.
Similarly, participating in experiences facilitating social healing stemming from sharing and understanding other cultures’ stories, art forms, beliefs, aspirations, lifestyles and realities can contribute to the types of transformative outcomes they seek. The NT already holds the ingredients that can be connected to inspire visitors and create outstanding and unique experiences for those seeking to broaden their horizons. Aboriginal tourism products targeting wellness transformation visitors must cater for visitors intangible (inspiration, genuine connections, cultural sharing, spiritual wellbeing) and tangible needs (service components8).
An example of product for wellness transformation visitors:
The NT offers unique traditional Aboriginal food experiences.
- These convey the rich traditions and cultural protocols passed down through generations.
- They reflect the cultural heritage and deep connections to the land.
- They demonstrate the enduring significance of “local Bush food”, including land and aquatic animals or plants in those distinct
- Aboriginal people’s diets and cultural lives. Furthermore, they take place in settings where the connections between culture, tradition, landscape/country and food can be experienced by wellness transformation visitors.9
